AAM - Pratt & Whitney Engines
| 1st Run |
Brand | Name | Model | HP | Weight | Built | |
| 1925 | P&W | Wasp | R-1340 | 450 to 600 | 930 | 34,966 | Used on: Fairchild 71 - Black wood stand, NE corner Odom Hangar |
| 1925 | P&W | Wasp | R-1340 | 450 to 600 | 930 | 34,966 | Used on: Noorduyn Norseman |
| 1925 | P&W | Wasp | R-1340 | 450 to 600 | 930 | 34,966 | Used on: Pilgrim 100B |
| 1925 | P&W | Wasp | R-1340-C | 450 | 930 | 34,966 | On blue engine stand, ignition wires, no sign, ASM 92-21-14 Middle Hangar |
| 1926 | P&W | Hornet | R-1690 | 780 | 1,014 | 2,944 | Used on: Sikorsky S-43 On blue engine stand, sign that says it was used on Pilgrim |
| 1926 | P&W | Hornet | R-1690-B | 780 | 1,014 | 2,944 | Black engine mount, oil pan on pallet - Odom Hangar |
| 1929 | P&W | Wasp Junior | R-985 | 450 | 640 | ≈39,000 | Used on: Beechcraft Model 18 |
| 1929 | P&W | Wasp Junior | R-985 | 450 | 640 | ≈39,000 | Used on: Grumman Goose |
| 1929 | P&W | Wasp Junior | R-985 | 450 | 640 | ≈39,000 | Used on: Travelair 6000B |
| 1937 | P&W | Double Wasp | R-2800 | 1,500 to 2,800 | 2,360 | 125,334 | Used on: Douglas DC-6 |
| 1944 | P&W | Wasp Major | R-4360 | 4,300 | 3,720 | 18,697 | Used on: Fairchild C-119 Flying Boxcar |
| 1960 | P&W | JT8D-17 SER | 4,741 | Used on: Boeing 737 |
Pratt & Whitney Engines
| 1st Run |
Name | Model | HP | Weight | Built | ||
| 1925 | Wasp | R-1340 | 450 to 600 | 930 | 34,966 | Used on: Fairchild 71, Noorduyn Norseman, Pilgrim 100B, Grumman Mallard | |
| 1926 | Hornet | R-1690 | 780 | 1,014 | 2,944 | Larger version of the Wasp Used on: Sikorsky S-43 |
|
| 1929 | Wasp Junior | R-985 | 450 | 640 | ≈39,000 | Smaller version of the Wasp Used on: Beechcraft Model 18, Grumman Goose, Travelair 6000B, DHC-2 Beaver, Stinson Reliant, Waco S3HD |
|
| 1937 | Double Wasp | R-2800 | 1,500 to 2,800 | 2,360 | 125,334 | Used on: Douglas DC-6 | |
| 1944 | P&W | Wasp Major | R-4360 | 4,300 | 3,720 | 18,697 | Used on: Fairchild C-119 Flying Boxcar |
| 1960 | JT8D-17 SER | 4,741 | Used on: Boeing 737 | ||||
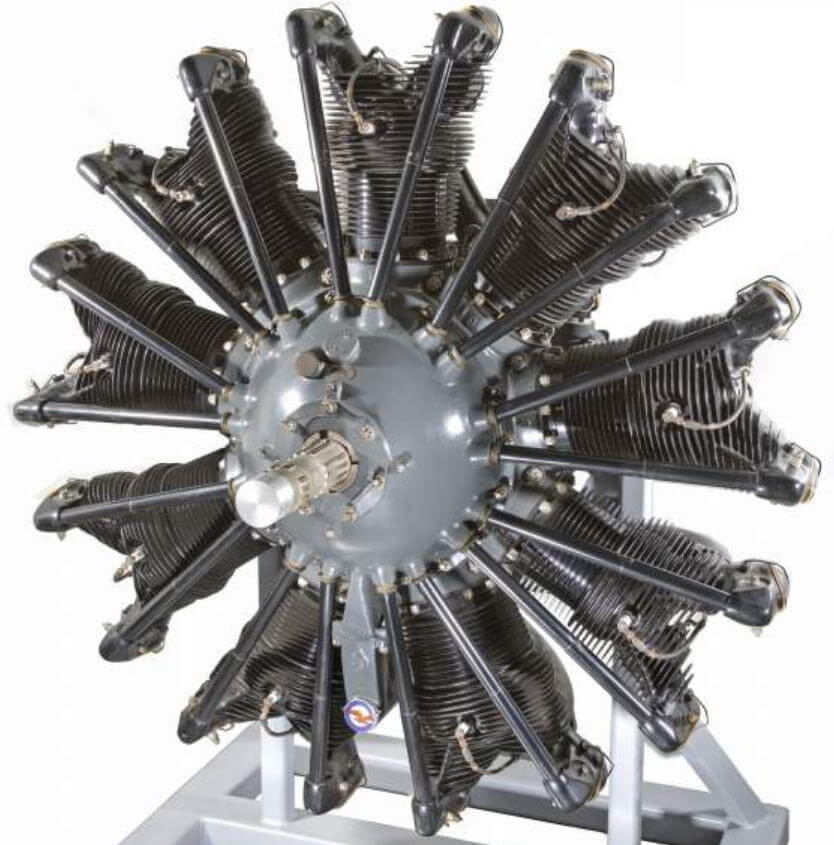
Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Wasp Engine
Pratt & Whitney's first engine was called the Wasp.
Completed on Christmas Eve of 1925, the Wasp was an air-cooled, radial piston engine with 1,340 cubic inches of displacement. It also featured a revolutionary design for the crankshaft and master rod, which eliminated what had proved to be a weak area in other engines. The new Wasp weighed less than 650 pounds.
The Wasp developed 425 horsepower on its third test run. It easily passed Navy qualification testing in March 1926, and by October of the same year, the Navy had ordered 200 engines. The Wasp demonstrated exceptional capabilities. It exhibited speed, rate of climb, performance at altitude and reliability that revolutionized American aviation, shattering one record after another. Soon it dominated Navy and Army Air Force fighter planes.
The Wasp also made its mark on early commercial aviation during the 1930s. Charles Lindbergh shattered the transcontinental speed record in 1930 with his Wasp-powered Lockheed Sirius. Jimmy Doolittle relied on his Wasp to take his Gee Bee aircraft to new speeds. And, Amelia Earhart made history with her Wasp-powered Lockheed Electra 10E.
Pratt & Whitney R-1340-S1H1-G Wasp |
||
| First Run: | 1925 | |
|---|---|---|
| Number Built: | 34,966 | |
| General Characteristics | ||
| Type: | Nine-cylinder single-row supercharged air-cooled radial engine | |
| Bore: | 5.75 in | 146 mm |
| Stroke: | 5.75 in | 146 mm |
| Displacement: | 1,344 cu in | 22 L |
| Diameter: | 51.75 in | 1,314 mm |
| Dry weight: | 930 lb | 422 kg |
| Components | ||
| Valvetrain: | 1 inlet and 1 exhaust valve per cylinder Pushrod-actuated | |
| Supercharger: | Single-speed centrifugal type supercharger, 1:10 step-up | |
| Fuel system: | Two-barrel Stromberg carburetor | |
| Fuel type: | 91 octane rating gasoline | |
| Cooling system: | Air-cooled | |
| Reduction gear: | 3:2 | |
| Performance | ||
| Power output: | 600 hp at 2,250 rpm at 6,200 ft | 447 kW (1,890 m) |
| 740 hp at 2,250 rpm at 7,000 ft (2,135 m) | 552 kW | |
| Specific power: | 0.45 hp/cu in | 20.3 kW/l |
| Compression ratio: | 6:1 | |
| Power-to-weight ratio: | 0.65 hp/lb at cruising rpm | 1.05 kW/kg |


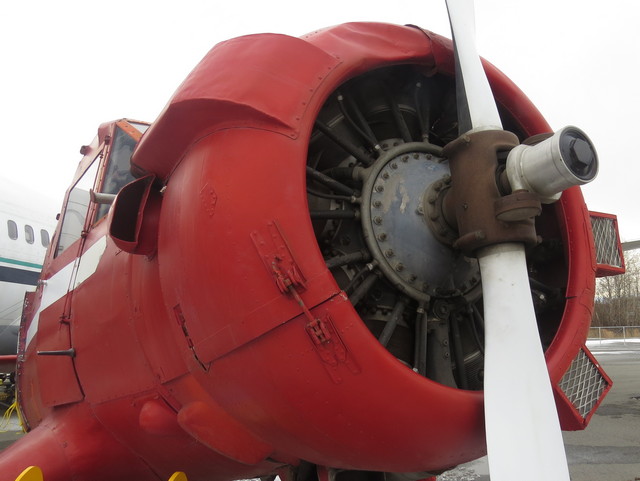
Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Wasp - Fairchild 71

This Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Wasp was removed from the Fairchild 71 owned by Bob Reeve.
Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Wasp - Pilgrim

550 hp (410 kW), 3:2 geared prop shaft
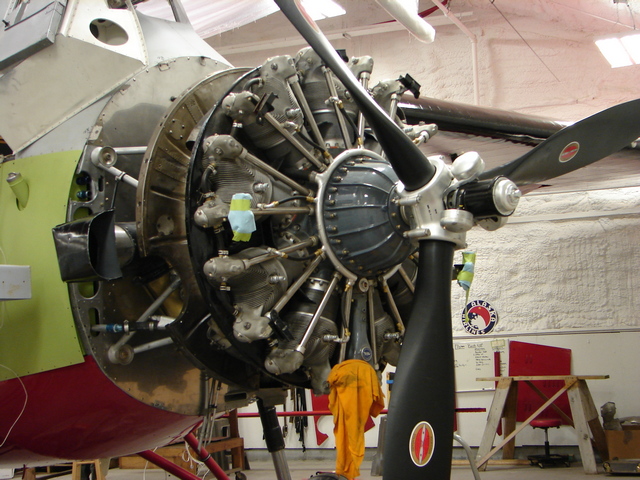
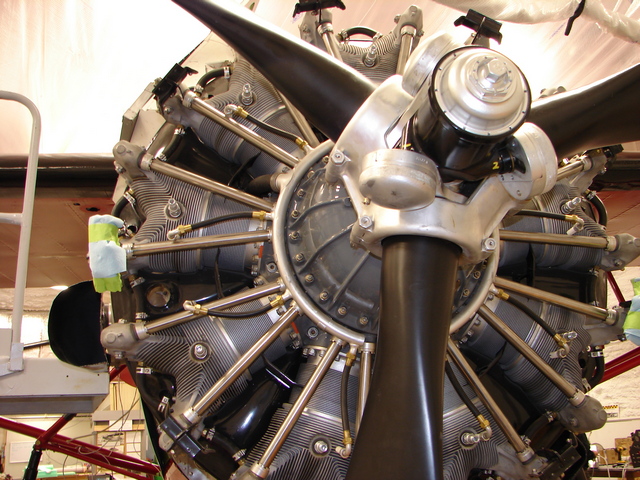
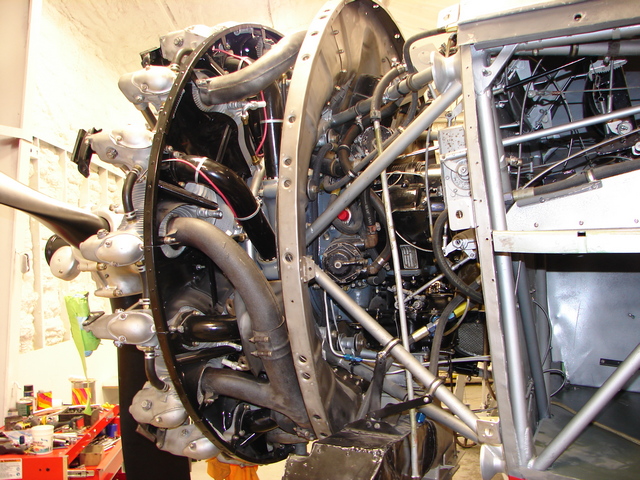

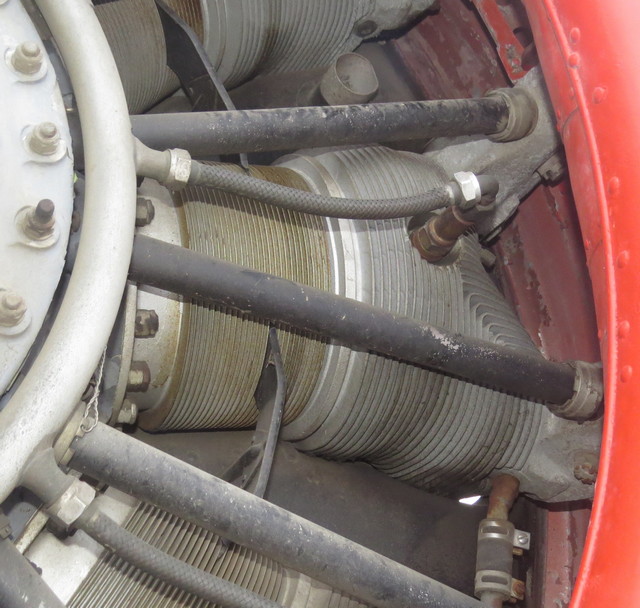
Pratt & Whitney R-1340-C Wasp Engine
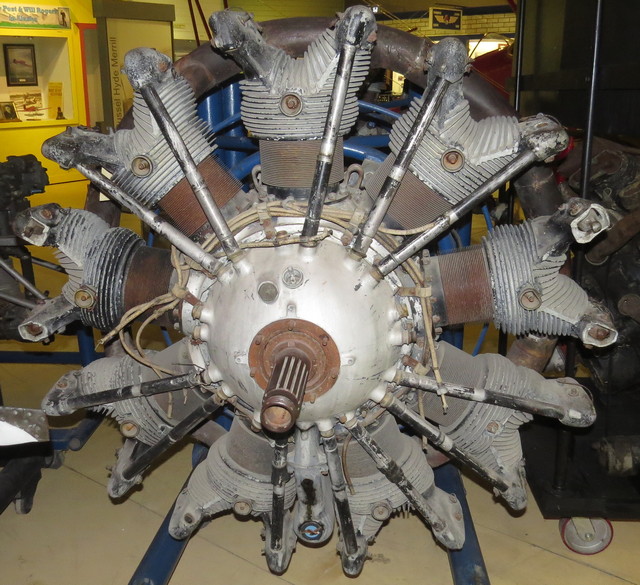




Tag numbers: TMA-76-17, ASM 92-21-14.
Data plate on right side of accessory case.
This is a single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled radial design.
450 HP at 2,100 rpm
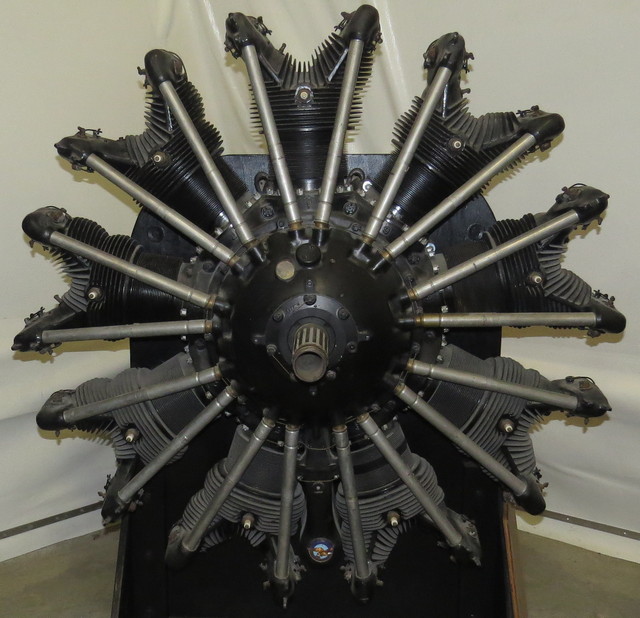
Pratt & Whitney R-1690 Hornet
2,944 were produced from 1926 through 1942. It is a single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled radial design. The B model is rated at 575 hp.
Pratt & Whitney R-1690 SIE-G |
||
| First Run: | 1926 | |
|---|---|---|
| Number Built: | 2,944 | |
| General Characteristics | ||
| Type: | Nine-cylinder single-row supercharged air-cooled radial engine | |
| Bore: | 6 1⁄8 in | 155 mm |
| Stroke: | 6 3⁄8 in | 161 mm |
| Displacement: | 1,690 cu in | 27.7 L |
| Length: | 50.98 in | 1,295 mm |
| Diameter: | 54.41 in | 1,382 mm |
| Dry weight: | 1,014 lb | 460 kg |
| Components | ||
| Valvetrain: | 1 inlet and 1 exhaust valve per cylinder Pushrod-actuated | |
| Supercharger: | Single-speed centrifugal type supercharger, 12.0:1 gear ratio | |
| Fuel system: | Two-barrel Stromberg carburetor | |
| Fuel type: | 87 octane rating gasoline | |
| Cooling system: | Air-cooled | |
| Reduction gear: | Epicyclic gearing, 2:3 | |
| Performance | ||
| Power output: | 789 hp at 2,300 rpm for takeoff | 589 kW |
| 740 hp at 2,250 rpm at 7,000 ft (2,135 m) | 552 kW | |
| Specific power: | 0.47 hp/cu in | 21.26 kW/l |
| Compression ratio: | 6.0:1 | |
| Specific fuel consumption: | 0.6 lb/(hp•h) | 362 g/(kW•h) |
| Oil consumption: | 0.42 oz/(hp•h) | 16 g/(kW•h) |
| Power-to-weight ratio: | 0.78 hp/lb at cruising rpm | 1.28 kW/kg |
Pratt & Whitney Hornet Engine
On blue engine stand, sign that says it was used on Pilgrim
“Fairchild” written in marker on flattened cowl
525 HP at 1,900 rpm
Two data plates on right side of accessory case. Top for GE supercharger, bottom for engine.
ASM 92-21-13




Pratt & Whitney R-1690-B Hornet


2,944 were produced from 1926 through 1942. It is a single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled radial design. The B model is rated at 575 hp.
On black engine mount, oil pan, on pallet
US ARMY AIR CORPS
TYPE: R-1690-B
SERIAL NO: 30-760
DATE ACCEPTED: 10-9-30
The ‘TYPE’ of ‘R-1690-B’ on this engine data plate was hard to find. When you Google it, you almost always get redirected to the Pratt & ‘Whitney R-1860-B Hornet’. Two foreign language versions of the R-1690 page mention that the ‘R-1690-B’ variation puts out 575 hp (429 kW)
According to the Virtual Aircraft Museum, in 1930, in Finland, there were five VL Kotka (Eagle) open-cockpit biplane maritime patrol aircraft produced with an R-1690-B engine. The remains of one is on display at the Paijat-Hame Museum.
In 1931, the prototype for the Douglas T3D, a three place open-cockpit biplane torpedo bomber originally used an R-1690-B engine, but it was later replaced with a R-1830 engine. The T3D never made it into production.
There was one mention of a US government purchase in a Google scanned magazine:
U.S. Air Services - Volume 16 - Page 58 -June 1931
“Devoted to the Development of Aeronautics - Civil and Military - in the United States, Birthplace of the Flying Machine, and Throughout the World”
Contract awards were announced on May, 23 by the War Department:
Pratt & Whitney Aircraft Company, Hartford — Thirty Hornet type R-1690-B engines and spare parts; total, $174,591.39.
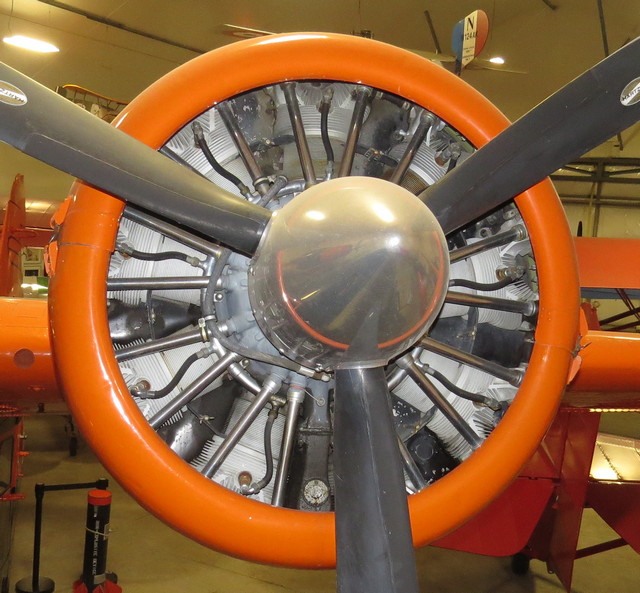
1929 Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior
Smaller version of the Wasp
Used on: Beechcraft Model 18, Grumman Goose, Travelair 6000B DHC-2 Beaver, Stinson Reliant, Waco S3HD
The Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior is a series of nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engines built by the Pratt & Whitney Aircraft Company from the 1930s to the 1950s.
These engines have a displacement of 985 cu in (16 L); initial versions produced 300 hp (220 kW), while the most widely used versions produce 450 hp (340 kW).
Wasp Juniors have powered numerous smaller civil and military aircraft, including small transports, utility aircraft, trainers, agricultural aircraft, and helicopters. Over 39,000 of these engines were built, and many are still in service today.
Pratt & Whitney Wasp Junior SB |
||
| First Run: | 1929 | |
|---|---|---|
| Number Built: | ≈39,000 | |
| General Characteristics | ||
| Type: | 9-cylinder supercharged air-cooled radial piston engine | |
| Bore: | 5 3⁄16 in | 132 mm |
| Stroke: | 5 3⁄16 in | 132 mm |
| Displacement: | 985 cu in | 16.4 L |
| Length: | 41.59 in | 1,056 mm |
| Diameter: | 45.75 in | 1,162 mm |
| Dry weight: | 640 lb | 290 kg |
| Components | ||
| Valvetrain: | 1 inlet and 1 exhaust valve per cylinder Pushrod-actuated | |
| Supercharger: | Single-speed gear-driven General Electric centrifugal supercharger, with impeller driven at 10 times crankshaft speed | |
| Fuel type: | 80/87 octane rating gasoline | |
| Cooling system: | Air-cooled | |
| Reduction gear: | Direct drive | |
| Performance | ||
| Power output: | 450 hp at 2,300 RPM for takeoff | 336 kW |
| 400 hp at 2,200 RPM up to 5,000 ft (1,500 m) | 298 kW | |
| Specific power: | 0.406 hp/cu in | 18.5 kW/l |
| Compression ratio: | 6.0:1 | |
| Power-to-weight ratio: | 0.625 hp/lb at cruising rpm | 1.03 kW/kg |
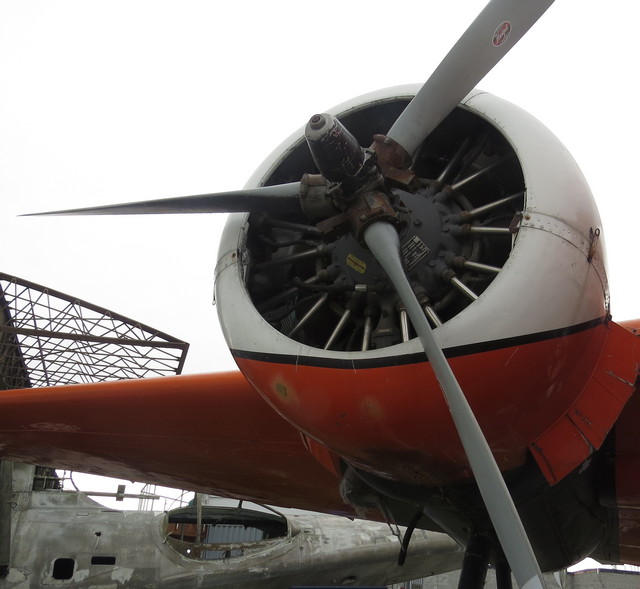
Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior - Beechcraft Model 18
More Wasp Junior details
The Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior is a series of nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engines built by the Pratt & Whitney Aircraft Company from the 1930s to the 1950s.

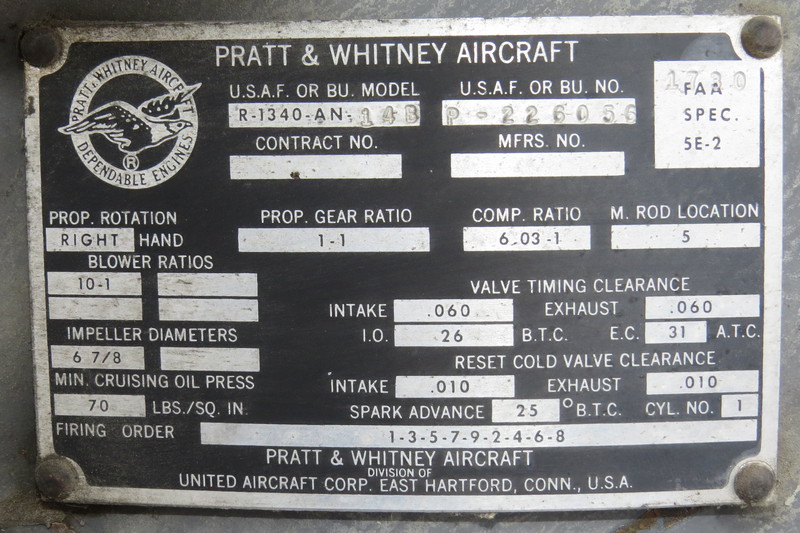

Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior - Grumman Goose
More Wasp Junior details
The Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior is a series of nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engines built by the Pratt & Whitney Aircraft Company from the 1930s to the 1950s.
Note that the engines are not the exact same models. Left Engine - R-985-AN-1, Right Engine - R-985-AN-14B

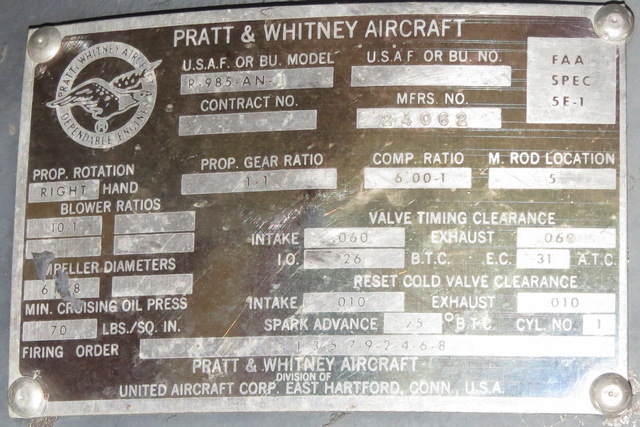

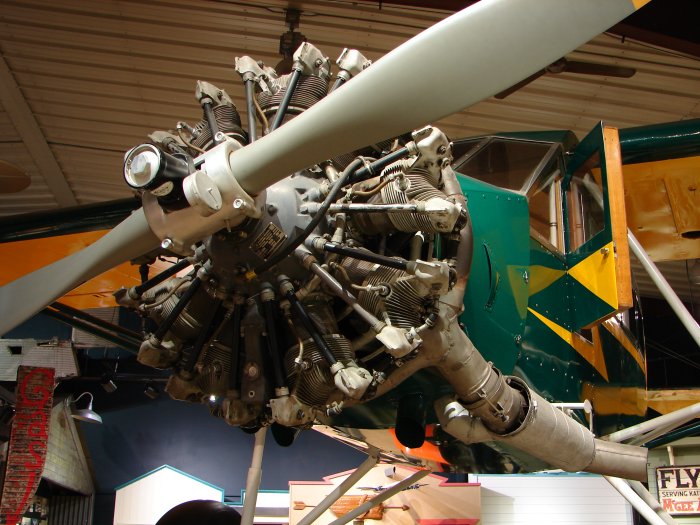
Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior - Travelair 6000B
More Wasp Junior details
The Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior is a series of nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engines built by the Pratt & Whitney Aircraft Company from the 1930s to the 1950s.


1937 Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp
Used on: Douglas DC-6
The Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp is an American twin-row, 18-cylinder, air-cooled radial aircraft engine with a displacement of 2,800 cu in (46 L), and is part of the long-lived Wasp family.
The R-2800 is considered one of the premier radial piston engines ever designed and is notable for its widespread use in many important American aircraft during and after World War II. During the war years, Pratt & Whitney continued to develop new ideas to upgrade this already powerful workhorse, most notably water injection for takeoff in cargo and passenger planes and to give emergency power in combat.
Pratt & Whitney R-2800-54 |
||
| First Run: | 1937 | |
|---|---|---|
| Number Built: | 125,334 | |
| General Characteristics | ||
| Type: | 18-cylinder air-cooled twin-row radial engine with water injection | |
| Bore: | 5.75 in | 146.05 mm |
| Stroke: | 6 in | 152.4 mm |
| Displacement: | 2,804.5 cu in | 45.96 L |
| Length: | 81.4 in | 2,068 mm |
| Diameter: | 52.8 in | 1,342 mm |
| Dry weight: | 2,360 lb | 1,073 kg |
| Components | ||
| Valvetrain: | Poppet, two valves per cylinder | |
| Supercharger: | Variable-speed (in F8F-2, unified with throttle via AEC automatic engine control), single-stage single-speed centrifugal type supercharger | |
| Fuel system: | One Stromberg injection carburetor | |
| Fuel type: | 100/130 octane gasoline | |
| Cooling system: | Air-cooled | |
| Performance | ||
| Power output: | 2,100 hp @ 2,700 rpm | 1,567 kW |
| Specific power: | 0.75 hp/cu in | 34.1 kW/L |
| Power-to-weight ratio: | 0.89 hp/lb | 1.46 kW/kg |
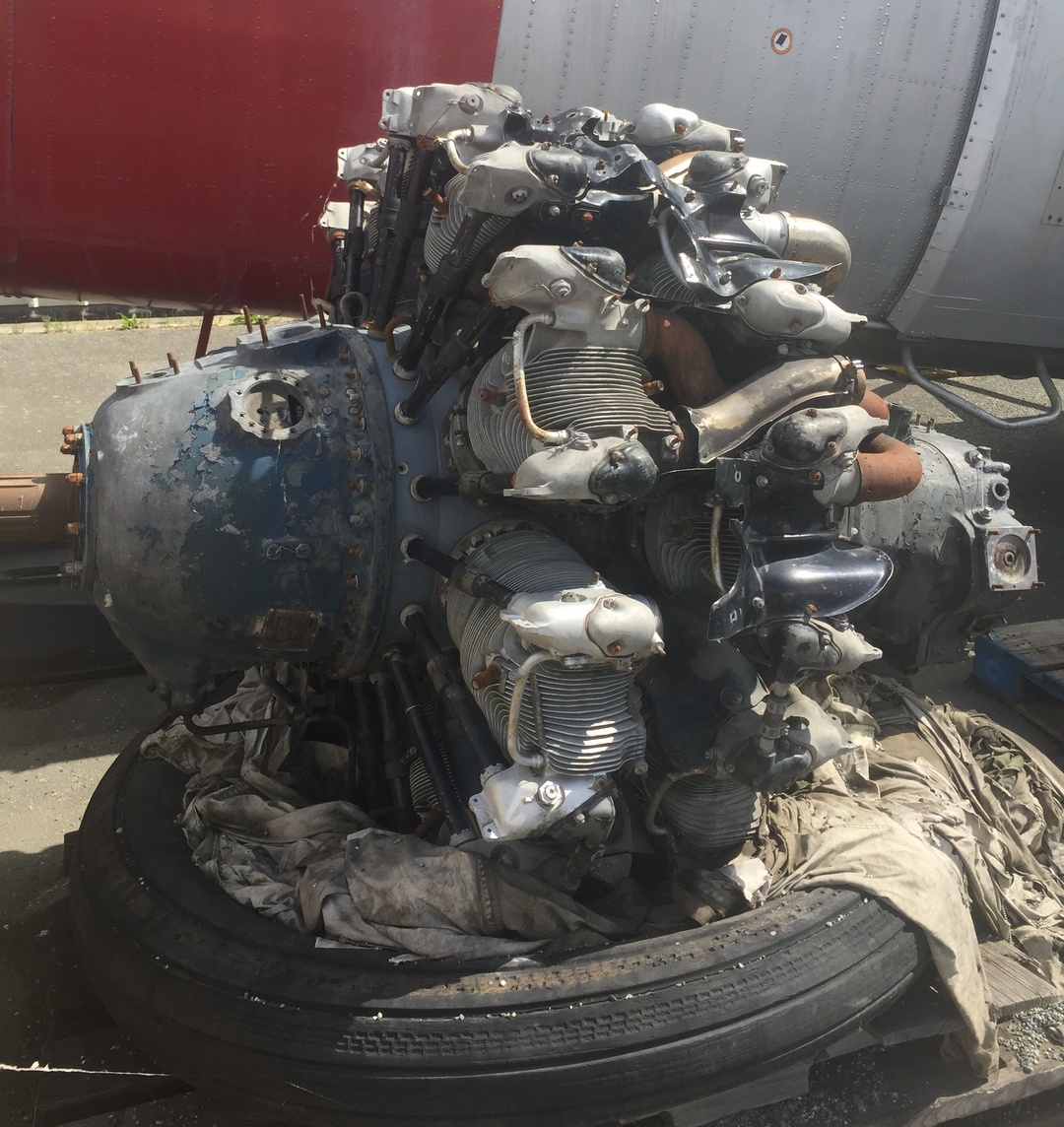


1944 Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major
Used on: Boeing 377, Boeing B-50 Superfortress, Boeing C-97 Stratofreighter, Convair B-36, Fairchild C-119 Flying Boxcar, Hughes H-4 Hercules ("Spruce Goose")
The Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major is an American four-row, 28-cylinder four-row radial piston aircraft engine designed and built during World War II, and the largest-displacement aviation piston engine to be mass-produced in the United States. It was the last of the Pratt & Whitney Wasp family, and the culmination of its maker's piston engine technology. The war was over before it could power airplanes into combat. It powered many of the last generation of large piston-engined aircraft before turbojets, and equivalent (and superior) horsepower turboprops (such as the Allison T56), supplanted it. Its main rival was the twin-row, 18-cylinder, nearly 3,350 cu in (54.9 l) displacement Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone, first run some seven years earlier (May 1937).
Pratt & Whitney R-4360-51VDT Wasp Major |
||
| First Run: | 1944 | |
|---|---|---|
| Number Built: | 18,697 | |
| General Characteristics | ||
| Type: | 28-cylinder air-cooled four-row radial engine | |
| Bore: | 5.75 in | 146.05 mm |
| Stroke: | 6 in | 152.4 mm |
| Displacement: | 4,362.5 cu in | 71.489 L |
| Length: | 103 in | 2,600 mm |
| Diameter: | 61 in | 1,500 mm |
| Dry weight: | 3,720 lb | 1,690 kg |
| Components | ||
| Valvetrain: | Poppet, two valves per cylinder | |
| Supercharger: | Gear-driven single stage variable speed centrifugal type supercharger | |
| Turbocharger: | General Electric CHM-2 (optional) | |
| Fuel system: | Bendix-Stromberg PR-100E2 pressure carburetor | |
| Fuel type: | 115/145 octane gasoline | |
| Oil system: | Dry sump | |
| Cooling system: | Air-cooled | |
| Performance | ||
| Power output: | 4,300 hp @ 2,800 rpm | 3,200 kW |
| Specific power: | 0.99 hp/cu in | 45 kW/L |
| Power-to-weight ratio: | 1.1 hp/lb | 1.82 kW/kg |
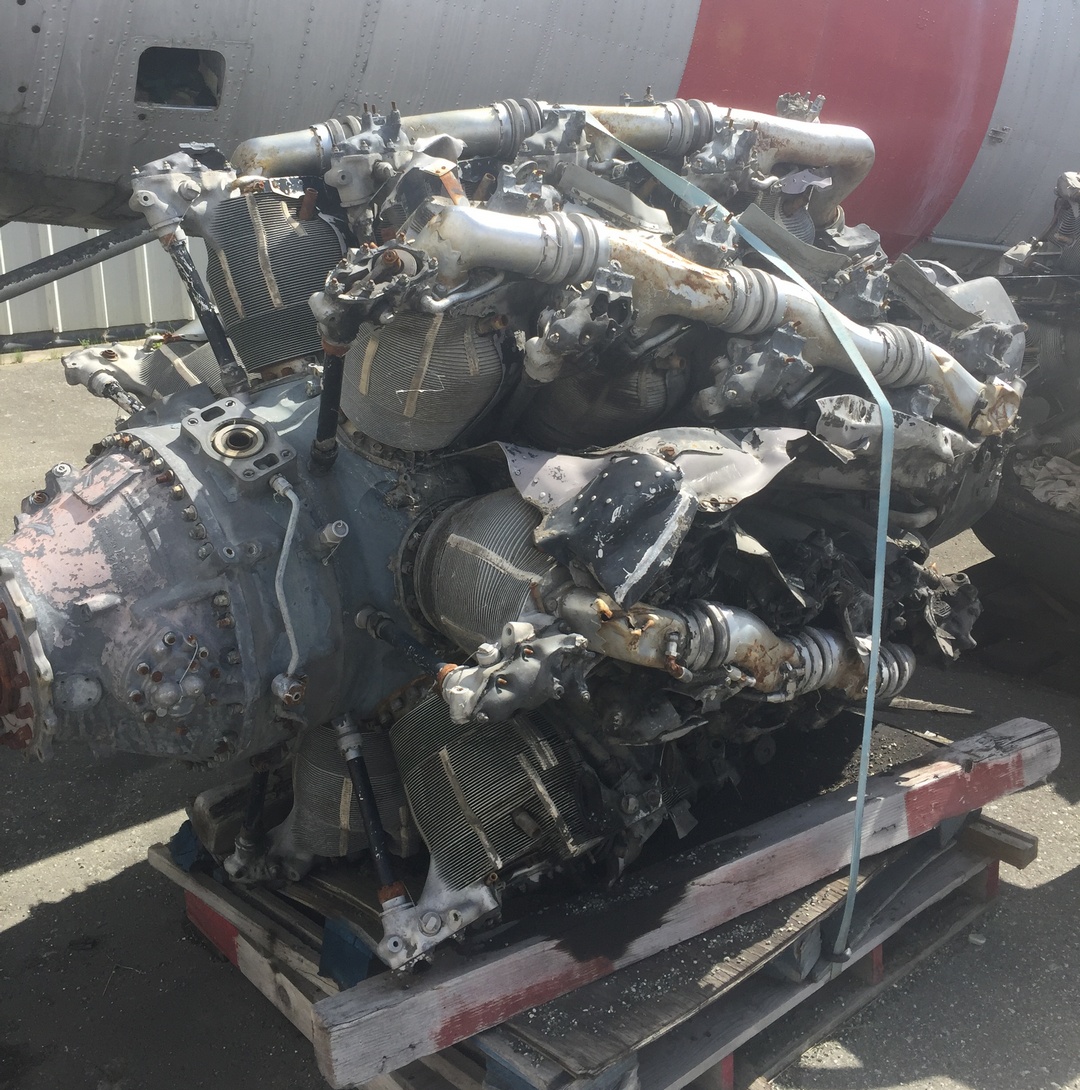

Pratt and Whitney JT8D-17 SER Engine

The Pratt & Whitney JT8D is a low-bypass (0.96 to 1) turbofan engine, introduced by Pratt & Whitney in February 1963 with the inaugural flight of the Boeing 727.
Used on: Boeing 737 Combi
(Wikipedia) - Pratt & Whitney JT8D turbo fan engine.
Pratt & Whitney JT8D-219 |
||
| First Run: | 1960 | |
|---|---|---|
| Number Built: | ||
| General Characteristics | ||
| Type: | Dual-spool, low-bypass-ratio turbofan | |
| Length: | 12 ft 10 in | 3.91 m |
| Diameter: | 49.2 in fan | 1.25 m |
| Dry weight: | 4,741 lb | 2,150 kg |
| Components | ||
| Compressor: | Axial flow, 1-stage fan, 6-stage LP, 7-stage HP | |
| Combustors: | Nine can-annular combustion chambers | |
| Turbine: | 3-stage (1 stage HP 3 stage LP) | |
| Fuel type: | 1 | |
| Oil system: | 2 | |
| Performance | ||
| Maximum thrust: | 21,000 lbf -200 series : 18,500-21,700 lbf | 93.4 kN |
| Overall pressure ratio: | 19.4 | |
| Air mass flow: | 331 lb/sec | |
| Fuel consumption: | 19% reduction over JT3D | |
| Specific fuel consumption: | 0.744 kg/daN.h | |
| Thrust-to-weight ratio: | 4.43 | |